The photoselective effects (UV Resistant) Greenhouse Film Usually used Effective UV Formulation Ratio.
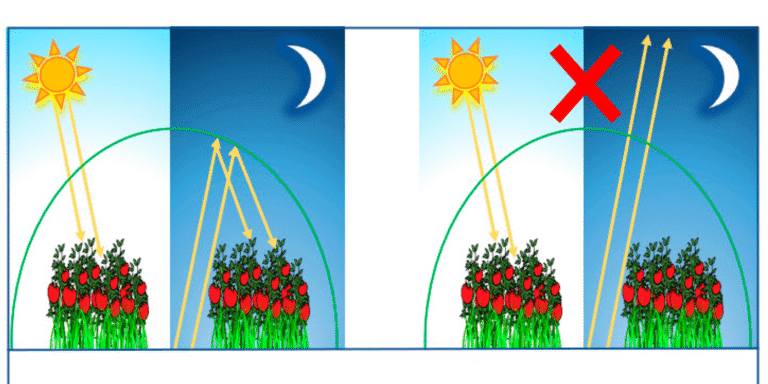
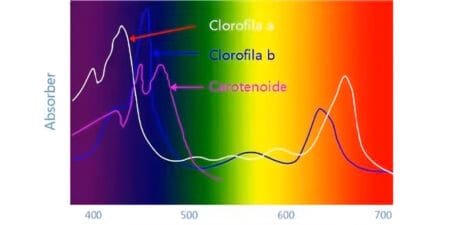
Light photoselective effects uses a highly efficient combination of organic and inorganic light-redirecting materials. It converts ultraviolet and yellow-green light, which are not absorbed by plant during photosynthesis, into blue-violet and red-orange light essential for plant growth. This enhances the photosynthetic capacity of crops, promotes growth, increases the chlorophyll, starch, and sugar content in plants, improves the absorption of nitrogen and other nutrients, ultimately leading to increased crop yield and quality.
UV Resistant
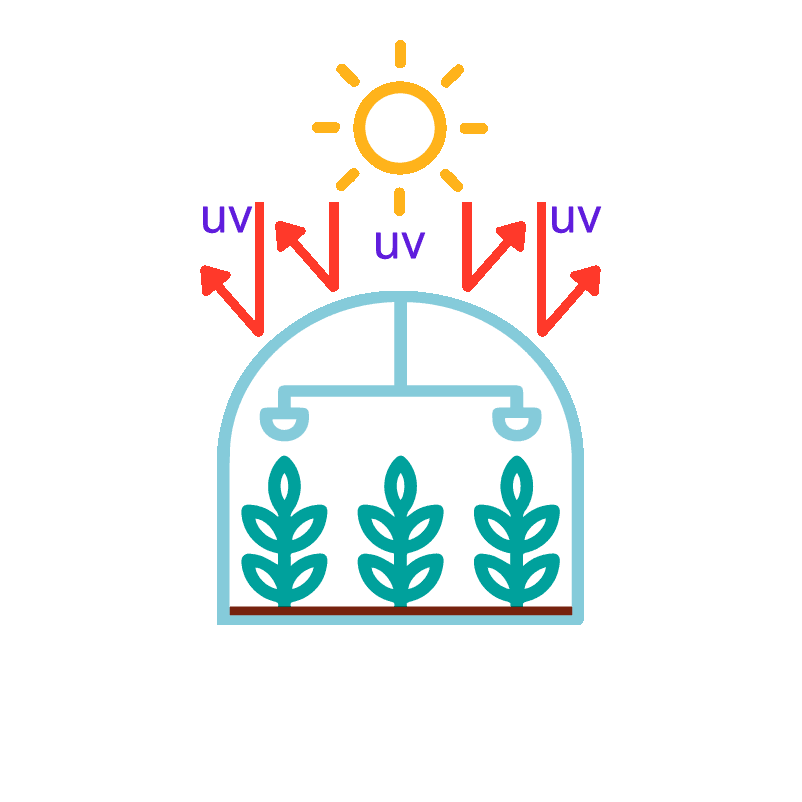
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a major factor in the aging of agricultural films. Light coversion additives convert UV light into red and blue light, thus reducing the impact of UV radiation on the service life of agricultural films.

Most pests are visually sensitive to short wavelengths of light. The reduction in UV light intensity within greenhouses using light-converting film, specifically in the 365-400nm range, causes pests to flee the greenhouse, thus reducing the incidence of pests and diseases. This is particularly suitable for pesticide-free vegetable cultivation.
The light-converting film boasts superior light conversion efficiency, maximizing the utilization of solar energy. The light-converting additive exhibits high efficiency at low temperatures, thus providing a warming effect. Conversely, its efficiency decreases at high temperatures, preventing excessive warming within the greenhouse under strong midday sun, thereby achieving a temperature-regulating effect.